近日,本研究中心在生物医学和健康信息学国际顶级期刊IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics (简写IEEE JBHI) 发表了题为 “Harmony Loss for Unbalanced Prediction” 的理论研究论文。博士研究生傅宇与薛鹏为该论文共同第一作者,董恩清教授为通讯作者,山东大学为唯一完成单位。
近年来,深度学习技术已经被广泛的应用在医学影像处理的各个领域,而不均衡样本预测问题一直制约深度学习发展的关键问题之一。有别于自然图像,医学影像本身数量较少,且稀有疾病类型相对于常见疾病类型的发病率低,这导致在医学影像数据中存在极大的类不均衡问题。此外,在医学影像分割或重建任务中,病变部位(或感兴趣区域)往往面积较小,导致医学影像内部像素之间也存在极大的类不均衡现象,这给基于深度学习的医学影像识别、分割或重建算法带来了极大的挑战。
为此,董恩清教授团队围绕深度学习在不均衡医学影像数据预测中面临的关键性难题,从损失函数的角度出发,依据Precision-Recall (PR)曲线的曲线下面积对每类样本都敏感的特性,提出了一个梯度稳定且计算效率高的调和损失函数 (Harmony loss)。通过大量实验认证,董恩清教授团队所提出的Harmony loss不仅极大提高了深度学习模型在不均衡医学影像分类任务中的准确率,而且在医学影像分割、医学影像重建等多个密集预测任务中同样有效。该研究成果不仅有效地解决了深度学习模型在不均衡医学影像数据中面临的关键性难题,而且适用于大部分常见的深度学习模型,属于基础理论研究成果。董恩清教授团队提出的Harmony loss损失函数是对交叉熵损失函数的进一步有效扩展,为不均衡数据预测问题中的深度学习方法研究奠定了坚实的理论基础。
IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics (简写IEEE JBHI)是公认的生物医学和健康信息学领域的TOP期刊,在全球27种医学信息学(Medical Informatics)SCI收录期刊中排名第1 (TOP1); 全球59种数学与计算生物学 (Mathematical & Computational Biology) SCI收录期刊中排名第5 (TOP5); 在全球109种计算机科学及交叉学科应用(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications) SCI收录期刊中排名第12 (TOP12); 在全球156种计算机科学及信息系统 (Computer Science, Information Systems) SCI收录期刊中排名第15 (TOP15); 中科院Medical Informatics和Mathematical & Computational Biology小类一区,2020年影响因子为5.772。
董恩清教授带领的医学影像信息处理研究团队聚焦国际上医工学科交叉研究领域中的热点问题,在图像识别、图像分割、图像配准、影像组学、AI医学影像诊断等方向取得了丰硕的研究成果。近年来,以山东大学作为独立作者单位,先后在IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging、IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics、Signal Processing、Medical Physics等国际顶级期刊 (JCR Q1)上发表高水平SCI论文10余篇,引起了国内外同行的广泛关注。
本项研究工作得到了国家自然科学基金面上项目资助 (2013、2016)、中央高校基本科研专项资金 (2019)、教育部高等学校博士学科点专项科研基金 (2012)。
论文链接:https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9477136 (Doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2021.3094578)
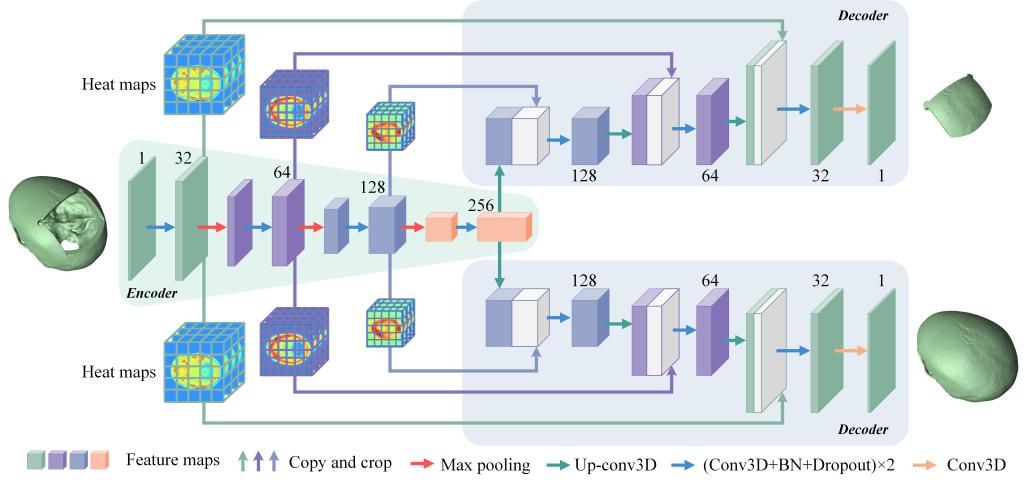
3D model for the reconstruction of defective skull. The number above each cube represents the number of feature maps in the corresponding layer.
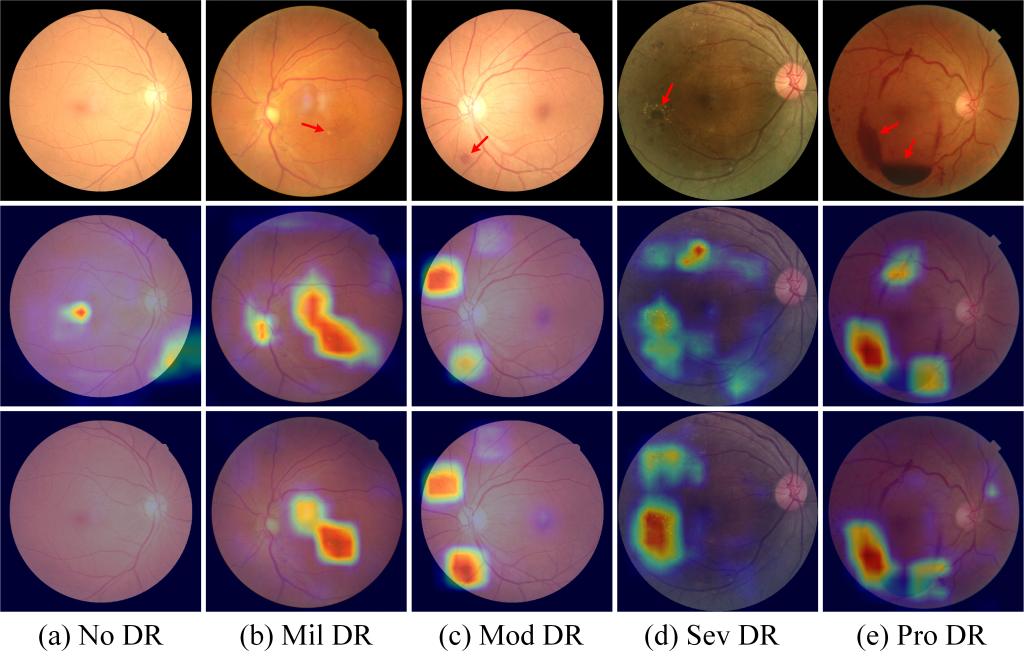
Visualization results of CE loss and Harmony loss on test set. The red arrows point to the lesion areas. From left to right, the images show the DR grading from light to severe. The second row is the results of CE loss, and the bottom row is the results of the Harmony loss.
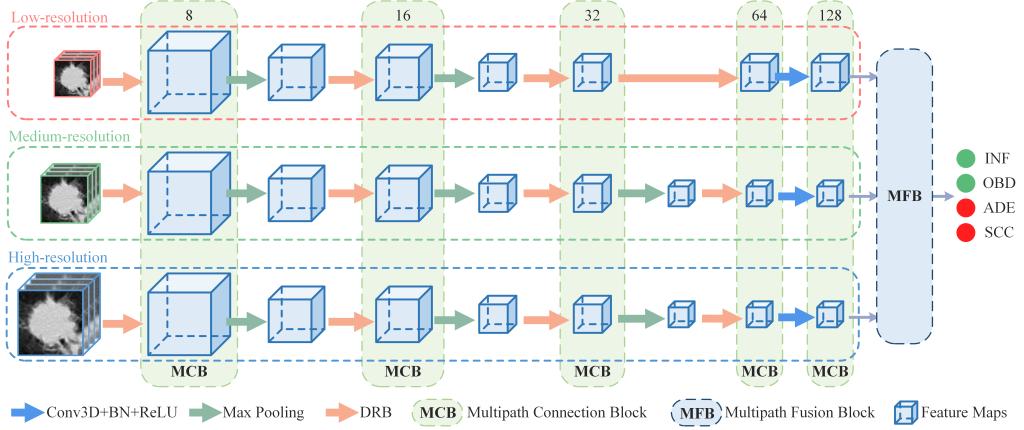
The structure of MF-Net. MF-Net takes the volume data of three different resolutions as inputs, and since the input size of the low-resolution path is small, only two max pooling operations were performed in the low-resolution path, while three max pooling operations were performed in other two paths. The number in the MCB represents the number of feature maps in current layer.
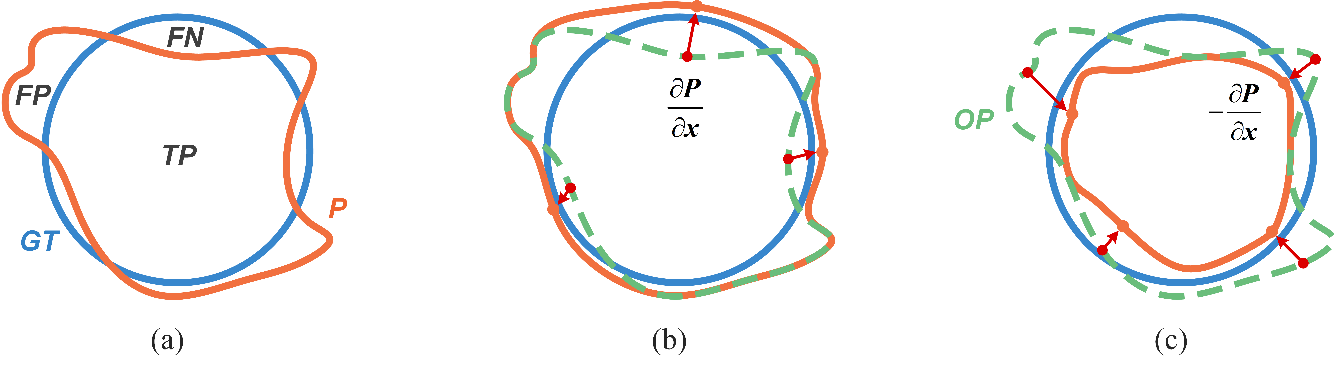
The predicted and true distribution of samples. The blue line and its interior represent ground truth (GT), the orange line and its interior represent predicted distribution (P), the green dashed line represents original predicted distribution boundary (OP), and the red arrow represents the change trend of the prediction value with different constraints.




